If you use a program or visit a website regularly in Windows 7, you may want to pin it to the Start menu or Taskbar for quicker access. When you pin a program or website to the Start menu or Taskbar, you can always see it there and easily access it with a single click. Windows 7 also includes Jump Lists, so that in addition to launching a program from the Start menu or Taskbar, you can now launch favorite and recent items from that program just by clicking the same button.
Pin a program to the Taskbar
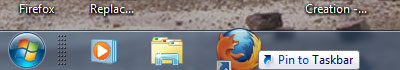
You can pin a program directly to the Taskbar, so you can open it quickly and conveniently, rather than looking for the program in the Start menu.
How to pin a program to the Taskbar
If the program is already running, right-click the program's button on the Taskbar (or drag the button toward the desktop) to open the program’s Jump List, and then click Pin this program to Taskbar.
or
If the program isn't running, click Start, find the program’s icon, right-click the icon, and then click Pin to Taskbar.
You can also pin a program by dragging the program's shortcut from the desktop or Start menu to the Taskbar. Additionally, if you drag the shortcut of a file, folder, or website to the Taskbar, and the associated program isn't already pinned there, then that program is pinned to the Taskbar, and the item is pinned to the program’s Jump List.
Notes:
To remove a pinned program from the Taskbar, open the program's Jump List, and then click Unpin this program from Taskbar.
Folders and shortcuts to folders appear in the Windows Explorer Jump List when opened or pinned.
You can pin a program from the Start menu to the Taskbar, but not from the Taskbar to the Start menu.
Pin a program to the Start menu

You can pin a program to the top of the Start menu so that you can open those programs quickly and conveniently.
How to pin a program to the Start menu
Click Start, find the program, right-click it, and then click Pin to Start Menu.
or
Click Start, finding the program, and then dragging it to the top left section of the Start menu.
The program's icon appears at the top of the Start menu.
Geek Tip:
You might decide to pin frequently-used programs to the Taskbar and occasionally-used programs to the Start menu.
Note:
Jump Lists contain recently-opened items and appear on the Start menu next to pinned and recently-used programs. You can pin items to Jump Lists.
Pin a website to the Taskbar
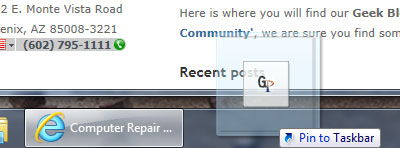
You can also pin a frequently visited website to the Taskbar, just like you would a program.
How to pin a website to the Taskbar
Click the webpage's tab and drag it to the Taskbar.
To remove a pinned website from the Taskbar:
Right-click the website icon on the Taskbar, and then click Unpin this program from Taskbar.
Using Jump Lists to open programs and items
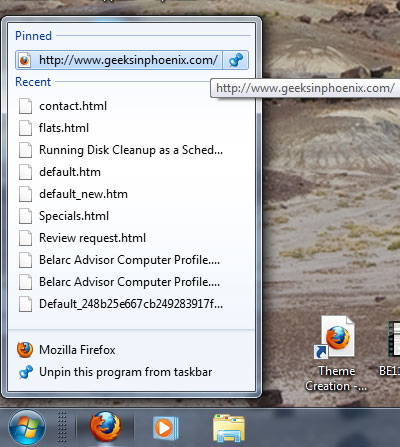
Jump Lists are lists of recently or frequently opened items, such as files, folders, tasks, or websites, organized by the program you use to open them. In addition to being able to open recent items using a Jump List, you can also pin favorite items to a Jump List so you can quickly get to the items that you use every day.
On the Taskbar, Jump Lists appear for programs that you've pinned to the Taskbar and programs that are currently running. You can view the Jump List for a program by right-clicking the Taskbar button or dragging the button toward the desktop. You open items from the Jump List by clicking them.
Managing programs and items with Jump Lists
On the Taskbar, Jump Lists appear for programs that you've pinned to the Taskbar and programs that are currently running. On the Start menu, Jump Lists appear for programs you've pinned to the Start menu and programs you've opened recently. (Jump Lists don't appear in All Programs on the Start menu.)
Jump Lists can include recently opened items, frequently opened items, tasks, or websites, in addition to any items that you've pinned.
You'll always see the same items in the Jump List for a program, regardless of whether you view the list on the Start menu or the Taskbar. For example, if you pin an item to a program’s Jump List on the Taskbar, it also appears in that program's Jump List on the Start menu.
Notes:
In addition to any pinned or currently open items, Jump Lists on the Taskbar contain several commands that you can use to close an item or unpin the program from the Taskbar.
You can drag an item from a Jump List to copy it to another location. For example, you can drag a document from a Jump List to an e-mail message if you want to send it to someone.
Working with Jump Lists on the Start menu
Jump Lists on the Start menu give you quick access to the things you use most often.
To view the Jump List for a program:
Click Start, point to a pinned program or a recently used program near the top of the Start menu, and then point to or click the arrow next to the program.
To open an item:
Click Start, point to a pinned program, or to a recently used program near the top of the Start menu to open the program's Jump List, and then click the item.
To pin an item to a Jump List:
- Click Start, and then open the program's Jump List.
- Point to the item, click the pushpin icon and then click Pin to this list.
To unpin an item:
- Click Start, and then open the Jump List for the program.
- Point to the item, click the pushpin icon and then click Unpin from this list.
Note:
The next time you open an item that you've unpinned, it might reappear in the Jump List. To remove an item from the list, right-click the item, and then click Remove from this list.
Working with Jump Lists on the Taskbar
Jump Lists on the Taskbar give you quick access to the things you use most often.
To view the Jump List for a program:
Right-click the program's button on the Taskbar.
To open an item from a Jump List:
Open the program's Jump List, and then click the item.
To pin an item to a Jump List:
Open the program's Jump List, point to the item, click the pushpin icon, and then click Pin to this list.
Notes:
You can also drag a file icon or a shortcut from the Start menu or the desktop to the Taskbar. This pins the item to the Jump List and also pins the program to the Taskbar if it isn't pinned already.
Folders are considered Windows Explorer items and appear in the Windows Explorer Jump List when pinned or opened.
To unpin an item:
Open the program's Jump List, point to the item, click the pushpin icon, and then click Unpin from this list.
Note:
The next time you open an item that you've unpinned, it might reappear in the Jump List. To remove an item from the list, right-click the item, and then click Remove from this list.