During your computer's regular use, you will accumulate several unnecessary files (temporary setup/internet files, recycle bin, etc.). You can remove these files with the built-in Disk Cleanup (cleanmgr.exe) utility inside of Windows 7. And it can be run a couple of different ways and with different options.
Running Disk Cleanup (cleanmgr.exe) on demand
There are a couple of different ways to run Disk Cleanup on demand. The following procedure cleans up files associated with your user account. You can also use Disk Cleanup to clean up all the files on your computer.
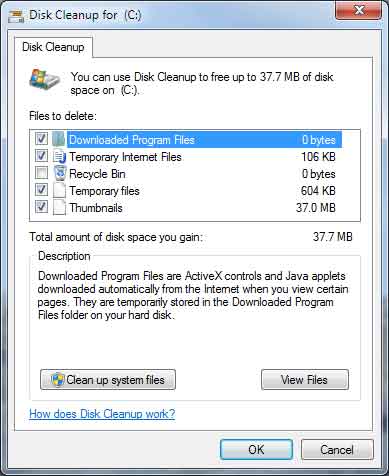
Windows 7 Disk Cleanup dialog box with standard options
- Click Start, and then type Disk Cleanup in the Start Search box.
or
Click Start, then All Programs, then Accessories, then System Tools, then Disk Cleanup
- In the Drives list, click the hard disk drive that you want to clean up, and then click OK
- In the Disk Cleanup dialog box, on the Disk Cleanup tab, select the checkboxes for the file types that you want to delete, and then click OK
- In the message that appears, click Delete files
The More Options tab is available when you choose to clean files from all users on the computer. This tab includes two additional ways to free even more disk space:
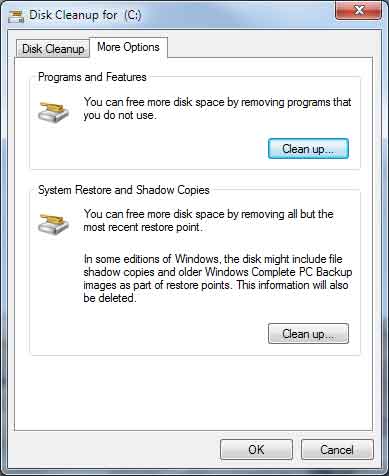
Windows 7 Disk Cleanup dialog box with more options
- Programs and Features. This option opens Programs and Features in Control Panel, where you can uninstall programs that you no longer use. The Size column in Programs and Features shows how much disk space each program uses.
- System Restore and Shadow Copies. With this option, you can delete all but the most recent restore point on the disk.
System Restore uses restore points to return your system files to an earlier point in time. If your computer is running normally, you can save disk space by deleting the earlier restore points.
In some editions of Windows 7, restore points can include previous versions of files, known as shadow copies, and backup images created with Windows Complete PC Backup. These files and images will also be deleted.
Running Disk Cleanup (cleanmgr.exe) as a scheduled task
You can also run Disk Cleanup from a command prompt. This gives you a few more options, like predefined settings for running Disk Cleanup as a scheduled task in Task Scheduler. First, we need to bring up a command prompt.
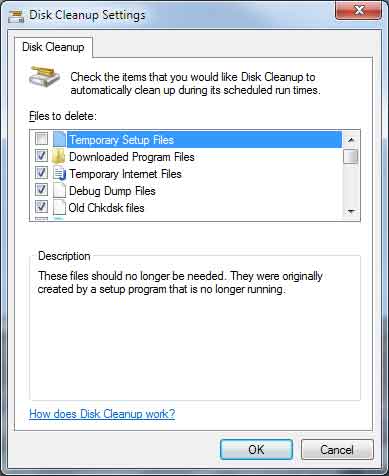
Windows 7 Disk Cleanup dialog box with sageset options
- Click Start, and then type cmd in the Start Search box.
- In the search results list, right-click Command Prompt, and then click Run as Administrator.
- If you are prompted by User Account Control, click Continue.
You can start the Disk Cleanup tool by running cleanmgr.exe. Disk Cleanup supports the following command-line switches:
- cleanmgr /d driveletter: - This switch selects the drive that you want Disk Cleanup to clean. Note that the /d switch is not used with /sagerun:n.
- cleanmgr /sageset:n - This switch displays the Disk Cleanup Settings dialog box and creates a registry key to store the settings you select. The n value is stored in the registry and allows you to specify different tasks for Disk Cleanup to run. The n value can be any integer value from 0 to 65535. To get all the available options when you are using the /sageset switch, you may need to specify the drive letter that contains the Windows installation.
- cleanmgr /sagerun:n - This switch runs the specified tasks that are assigned to the n value by using the /sageset switch. All drives in the computer will be enumerated, and the selected profile will be run against each drive.
How to run Disk Cleanup (cleanmgr.exe) on-demand and as a scheduled task inside of Windows 7.
87889aa6-3fab-4d8a-98c1-7a8f4013731d|0|.0|96d5b379-7e1d-4dac-a6ba-1e50db561b04