Updated August 12, 2020
Backing up your computer has never been exciting, but it needs to be done regularly. And with the increase of file-encrypting malware, having a good backup has never been more critical. Here's how to back up your files with File History and Windows Backup in Windows 10.

Windows 10 backup basics
Now there are two (2) different backup programs inside of Windows 10, Windows Backup, and File History, and each one does a specific type of backup. Windows Backup is geared more towards scheduled backups (nightly, weekly, etc.) and is usually used for full system backups / complete 'bare metal' system images. File History is more for personal files that frequently change, like Word documents and Excel spreadsheets, as it saves multiple versions of the same file.
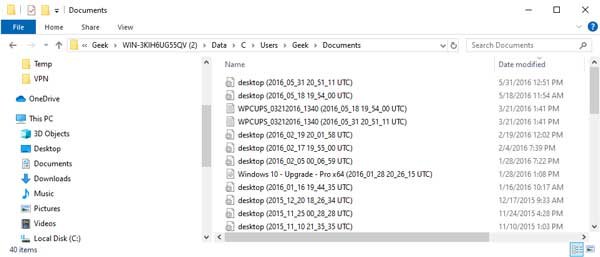
File History creates multiple versions of the same file with time-stamps in the names
The one thing that Windows Backup and File History have in common is that both of these programs can back up to an external drive or network folder. Windows Backup can also use writeable disks like CDs or DVDs.
With the recent outbreak of file-encrypting malware, if you're going to use a network folder, it is recommended you do not map a network folder to a drive letter (N:\Files), but instead use Uniform Naming Convention (UNC) (\\Server\Volume\Files).
Never use the same drive that Windows is installed on for File History or Windows Backup. If your computer gets a virus or the operating system gets corrupted, you may have to reformat the drive and reinstall Windows.
Remember, when not in use, store the media used for backups (external hard disks, DVDs, or CDs) in a secure place to prevent unauthorized people from having access to your files. It is also recommended to use a fire-proof location, like a data safe, to store the backup media.
Using File History to back up your files
File History will automatically create time-stamped versions of your files (documents, music, photos, etc.) on a set schedule. If the originals are lost, damaged, or deleted, you can restore them from an earlier point in time. You can schedule File History to run from every ten (10) minutes to daily. And you can also set the length time that File History keeps copies of your files, from 1 month to forever or whenever space is needed.
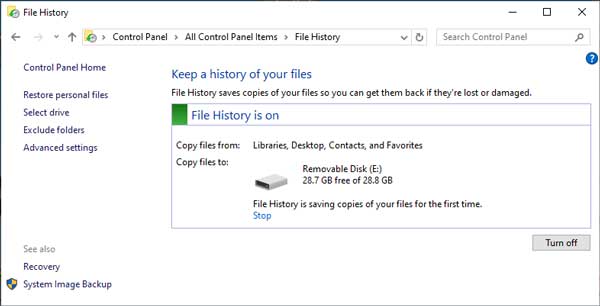
The main screen for File History
To use File History, you will need to either have an external drive or network folder to save the files. By default, File History will back up your folders (documents, photos, videos, etc.), but you can add additional folders to its configuration. Now configuring File History inside of Windows 10 can be a little confusing, as there are two (2) different places to change the settings, Settings and Control Panel.
How to open File History in Settings
- Left-click on the Start
 menu and select Settings (the gear icon).
menu and select Settings (the gear icon).
- Left-click on Update & security.
- In the left column, left-click on Backup.
How to open File History in the Control Panel
- Left-click on the Start
 menu.
menu.
- Scroll down to Windows System and left-click on it to expand it out.
- Left-click on Control Panel.
- If viewing by category, left-click on Save backup copies of your file with File History. If viewing by large/small icons, left-click on File History.
or
- In the search box next to the Start
 button, type Control Panel, and click on it from the results.
button, type Control Panel, and click on it from the results.
- If viewing by category, left-click on Save backup copies of your file with File History. If viewing by large/small icons, left-click on File History.
Here is a breakdown of what options can be changed and where to find them.
| File History option |
Settings |
Control Panel |
| Turn on or off |
X |
X |
| Manually run File History |
X |
|
| Change frequency (how often it runs) and duration (how long they are kept) of history |
X |
X |
| Add or remove folders |
X |
|
| Exclude folders (useful for sub-folders) |
X |
X |
| Change where backups are stored |
X |
X |
| Clean up older versions |
|
X |
| Restore files |
|
X |
Using Windows Backup to back up your files
The Windows Backup version included in Windows 10 is actually from Windows 7, hence the name in the Control Panel, Backup and Restore (Windows 7). If you used the version in Windows 7, everything will be familiar to you. With Windows Backup, you can back up just specific files and folders or do a complete system backup/system image. And you can schedule it to run whenever you want.
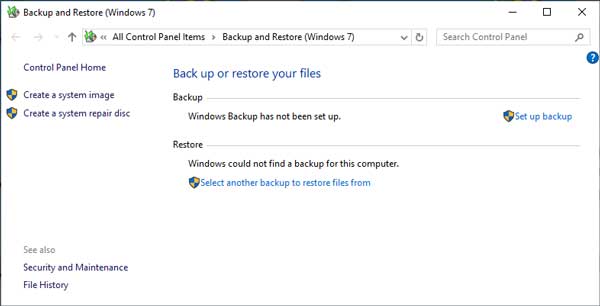
The main screen for Windows Backup
But unlike File History, Windows Backup creates a single backup that gets updated when it is run. No multiple file versions here, just the latest version of files at the time Windows Backup was run.
Along with using an external drive or network folder for backup, Windows Backup can also use CDs or DVDs. But if you're going to do a complete system backup on CD's or DVD's, be prepared with plenty of blank disks.
If you're creating a complete system image, remember to make a system repair disk to go along with it. If you ever need to restore your computer from a Windows Backup image, you will need to boot your computer from it. The link to create it is in the left-hand column.
How to open Windows Backup in Settings
- Left-click on the Start
 menu and select Settings (the gear icon).
menu and select Settings (the gear icon).
- Left-click on Update & security.
- In the left column, left-click on Backup.
- In the right column, left-click on Go to Backup and Restore (Windows 7).
How to open Windows Backup in the Control Panel
- Left-click on the Start
 menu.
menu.
- Scroll down to Windows System and left-click on it to expand it out.
- Left-click on Control Panel.
- Left-click on Backup and Restore (Windows 7).
or
- In the search box next to the Start
 button, type Control Panel, and click on it from the results.
button, type Control Panel, and click on it from the results.
- Left-click on Backup and Restore (Windows 7).
1f83178e-a697-4f5c-b96c-43ed0d0a586d|2|5.0|96d5b379-7e1d-4dac-a6ba-1e50db561b04