When your computer runs low on Random Access Memory (RAM), and more is needed to complete your current task, Windows uses hard drive space to simulate system RAM. In Windows, this is known as Virtual Memory and often called the Pagefile. The default size of the virtual memory pagefile (appropriately named Pagefile.sys) created during installation should be 1.5 times the amount of RAM on your computer.
You can optimize virtual memory use by dividing the space between multiple drives and removing it from slower or heavily accessed drives. To best optimize your virtual memory space, divide it across as many physical hard drives as possible. When selecting drives, keep the following guidelines in mind:
- Try to avoid having a pagefile on the same drive as the system files.
- Avoid putting a pagefile on a fault-tolerant drive, such as a mirrored volume or a RAID-5 volume. Pagefiles do not need fault-tolerance, and some fault-tolerant systems are slow because they write data to multiple locations.
- Do not place multiple pagefiles on different partitions on the same physical disk drive.
#1 - Find out how much RAM your computer has
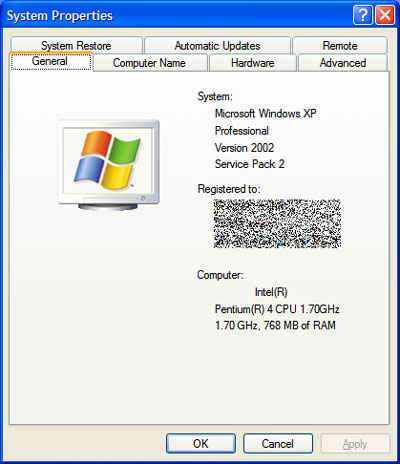
To open the System Properties, press  + Pause. In the System section, under Memory (RAM), you can view the amount of RAM your computer has.
+ Pause. In the System section, under Memory (RAM), you can view the amount of RAM your computer has.
#2 - change the size of the virtual memory paging file
You must be logged on as an administrator or a member of the Administrators group in order to complete this procedure. If your computer is connected to a network, network policy settings might also prevent you from completing this procedure.

- To open the System Properties, press
 + Pause
+ Pause
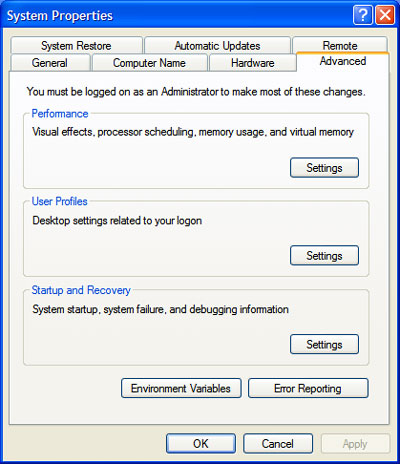
- On the Advanced tab, under Performance, click Settings.
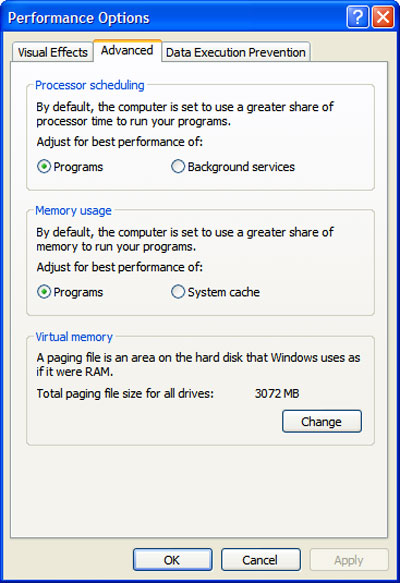
- On the Advanced tab, under Virtual memory, click Change.

- Under Drive [Volume Label], click the drive that contains the paging file you want to change.
- Under Paging file size for selected drive, click Custom size, and type a new paging file size in megabytes in the Initial size (MB) and Maximum size (MB) box, and then click Set. If you decrease the size of either the initial or maximum page file settings, you must restart your computer to see the effects of those changes. Increases typically do not require a restart.
Notes:
- To have Windows choose the best paging file size, click System managed size.
- For best performance, do not set the initial size to less than the minimum recommended size under Total paging file size for all drives. Use the following formula for calculating the correct pagefile size. Minimum pagefile size is one and a half (1.5) x amount of memory. Maximum pagefile size is three (3) x minimum pagefile size. Say you have 4 Gb (4,096 Mb) of memory. 1.5 x 4,096 = 6,144 Mb would be the min. pagefile size and 3 x 6,144 = 18,432 Mb would be the max. pagefile size. Usually, you should leave the paging file at its recommended size, although you might increase its size if you routinely use programs that require a lot of memory.
- To delete a paging file, set both initial size and maximum size to zero, or click No paging file. Microsoft strongly recommends that you do not disable or delete the paging file.
e9bfc9d6-0341-42f1-bdf9-575d49c945dd|0|.0|96d5b379-7e1d-4dac-a6ba-1e50db561b04