You hear these terms when you talk about computers: Megabyte, Gigabyte, Terabyte, 32-bit, 64-bit. For a novice computer user, these can be quite confusing. So, here's an explanation of a Bit and a Byte.
The terminology is familiar to almost everyone, but do you know what they are? To understand it, we have to go break it down to the primary 0's and 1's.
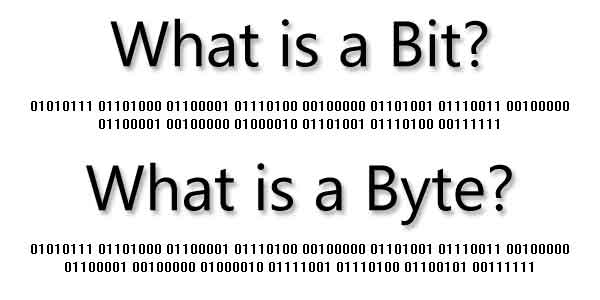
What is a Bit?
A Bit is the basic unit in computer information and has only two different values, generally defined as a 0 or 1. These values can be interpreted as on or off, yes or no, true or false, etc. It just depends on the binary code.
What is a Byte?
A Byte is just 8 Bits and is the smallest unit of memory that can be addressed in many computer systems. The following list shows the relationship between all of the different units of data.
| 0 (Off) or 1 (On) |
= |
1 Bit |
| 8 Bits |
= |
1 Byte |
| 1,024 Bytes |
= |
1 Kilobyte |
| 1,024 Kilobytes |
= |
1 Megabyte |
| 1,024 Megabytes |
= |
1 Gigabyte |
| 1,024 Gigabytes |
= |
1 Terabyte |
| 1,024 Terabytes |
= |
1 Petabyte |
| 1,024 Petabytes |
= |
1 Exabyte |
| 1,024 Exabytes |
= |
1 Zettabyte |
Let's take a look at a simple text file I created called sample.txt. It contains only eight (8) characters, four (4) upper case, and four (4) lower case letters. I created my text file using Notepad, so it is encoded using the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard binary code.
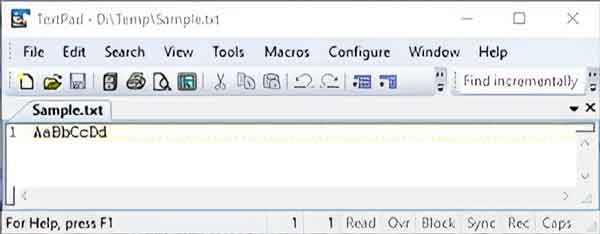
A sample text file with only eight characters opened in a text editor
The closest we can get to viewing raw binary code is to open my sample text file in a hexadecimal file editor. Hexadecimal digits allow for a more human-friendly representation of binary code.
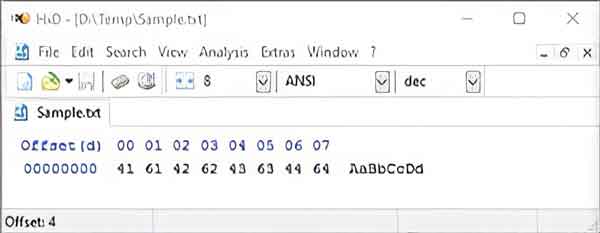
A sample text file with only eight characters opened in a hexadecimal editor
Since the ANSI code standard is a revision of the American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) code, we'll need to use that standard for references to binary information. Using the table of ASCII printable characters on Wikipedia, we can find the binary code equivalent.
| Character |
Hexadecimal |
Binary |
| A |
41 |
01000001 |
| a |
61 |
01100001 |
| B |
42 |
01000010 |
| b |
62 |
01100010 |
| C |
43 |
01000011 |
| c |
63 |
01100011 |
| D |
44 |
01000100 |
| d |
64 |
01100100 |
So, as you can see, each character contains 8 bits or 1 byte, and the whole sample.txt file is 8 bytes in size. To put this in perspective, I created a Microsoft Word document (sample.docx) with the same characters as the sample text file.
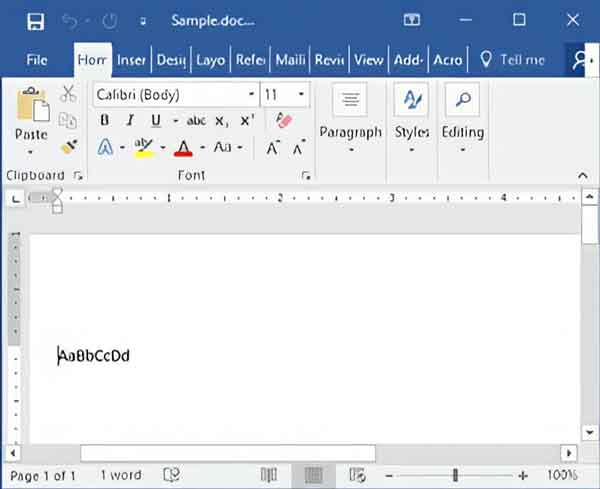
A sample Microsoft Word file with only eight characters opened in Microsoft Word
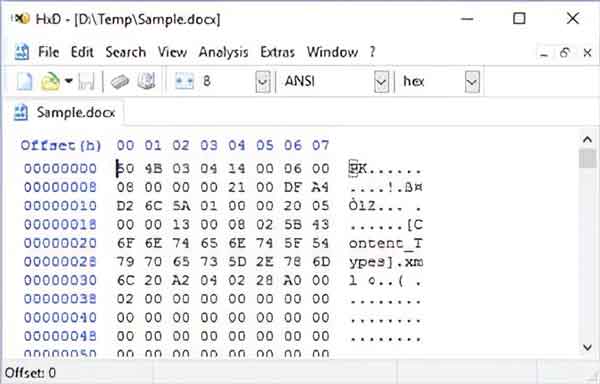
A sample Microsoft Word file with only eight characters opened in a hexadecimal editor
Here you can see all of the underlying formatting, and the size has increased significantly. The sample.docx file is almost 12 kilobytes (11,513 bytes) in size but contains only eight (8) characters.
What is 32-bit / 64-bit?
The terms 32-bit and 64-bit define the fixed-size piece of data a processor can transfer to and from memory. So, in theory, 64-bit computers can handle data twice as fast 32-bit systems.
The 32-bit computer architecture is most commonly known as x86 and was based on the Intel 8086 / 8088 processor. The Intel 8086 / 8088 processor was found in the original stand-alone Pac-Man video arcade console. The term for 64-bit computer architecture is x64, a little more straight forward.
The following Wikipedia articles were used for reference:
Bit - Wikipedia
Byte - Wikipedia
American National Standards Institute (ANSI) - Wikipedia
American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) - Wikipedia
Binary code - Wikipedia
Hexadecimal - Wikipedia
72fd31bc-af4c-4a2b-a757-8edac24beb17|1|5.0|96d5b379-7e1d-4dac-a6ba-1e50db561b04