Updated August 7, 2020
Internet browsers are prone to getting compromised. It can happen by opening an infected e-mail or viewing a malicious ad on a web page. But knowing how to get your browser back to normal is the key. Here's how to clean up and reset Google Chrome.
Of the top three (3) browsers out there, Google Chrome is the most popular. One of the main reasons is that to use Google's products, like Google Earth, you have to have Chrome installed. And since it is the most popular, it is also the biggest target for adware and malware. In fact, in the past, the Chrome web store has gotten compromised with infected apps. Google is now scrutinizing the Chrome extensions harder than ever because of it. So knowing how to clean up and reset Chrome comes in handy.
Cleaning up and resetting Chrome
Google has made resetting the Chrome browser reasonably simple. Just open Chrome and click on the Customize button in the upper right-hand corner (it looks like three (3) horizontal dots).
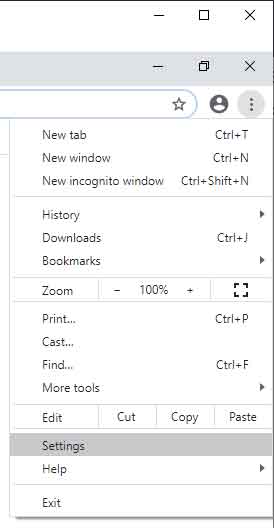
Go down and click on Settings, which will open a page with all user-configurable settings. On the left-hand column, you will find eleven (11) links: You and Google, Autofill, Safety check, Privacy and security,
Appearance, Search engine, Default browser, On startup, Advanced, Extensions, and About Chrome.
The Advanced link is a sub-menu that includes Languages, Downloads, Printing, Accessibility, System and Reset and cleanup. All of the links take you those sections on the Settings page except for Extensions and About Chrome. Those links go to separate pages.
The first section is You and Google. This is where you can synchronize Chrome (bookmarks, history, passwords, etc.) across multiple devices. If you are using Chrome on your computer and smartphone, this is a feature you may want to look into.
In this section, you can set up syncing all of the different Google services, adding a name and picture to your profile, and importing bookmarks and settings from other browsers.
The second section is Autofill. As the name suggests, you can choose if Chrome can store your data for online forms and what information it is allowed to save. Chrome can save and fill in passwords, payment methods, names, addresses, and e-mail addresses.
The next section is Safety check. When you click on the Check now button, Chrome checks for updates, insecure passwords, browsing protection, and harmful extensions.
Privacy and security is the next section. There are four categories: Clear browsing data, Cookies and other site data, Security, and Site settings. Let's look at each one separately.
The first category is Clear browsing data and is the first place I go when a customer complains about a website not functioning correctly. There are two categories here: Basic and Advanced.
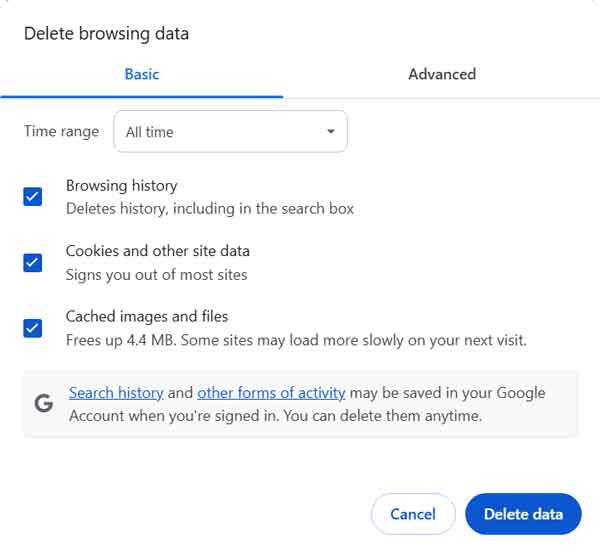
Quite often, just selecting the Basic settings with the Time range of All time will do the trick. If that does not fix things, try some of the Advanced options. I recommend doing one at a time until Chrome works the way you want.
The second category is Cookies and other site data. This where you define how Chrome handles cookies. The default setting is to block third-party cookies only when you use incognito mode and be perfectly safe.
You can completely block third-party or all cookies if you want, but I recommend turning on the Do Not Track option. Chrome does allow you to define what websites can and cannot use cookies. You can also specify what website cookies are cleared out when you close Chrome.
The third category is Security, and this is where you define how Chrome displays websites. The default setting for Safe Browsing is Standard protection and is recommended. You can use the Enhanced protection, but it does send browsing data back to Google. The rest of the default settings are recommended.
The fourth and last category is Site Settings. The default settings are recommended, but you can always modify them to your personal preferences. Some of these settings are actually in other sections, so don't be surprised if you see a setting you have already configured.
The next section is Appearance and is more for personalizing Chrome the way you want it to look. Just personal preferences here.
The Search engine section just defines what search engine Chrome will use in the address bar.
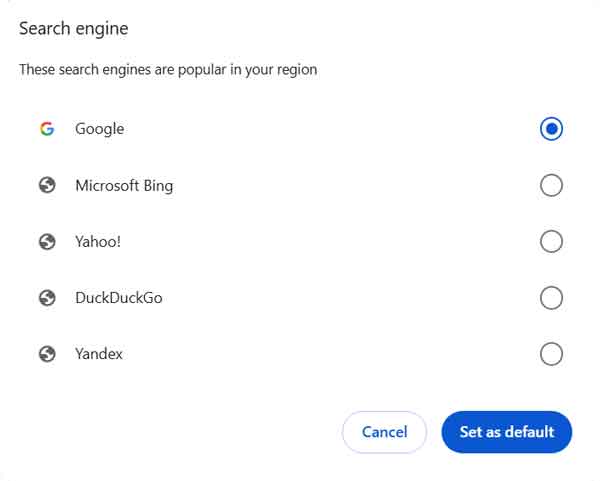
This is one place to check and see if your default search engine in Chrome has been hijacked. If you're not getting the search results you are expecting from the address bar,
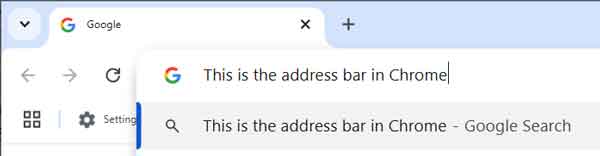
more than likely, your default search engine has been changed without your knowledge. You can add or remove any of the search engines on this list.
The Default browser section has a link to the Default apps so you can make Chrome your default browser.
The On startup section defines what pages are displayed when Chrome starts up and is one of the first places I look for evidence of browser hijacking. Allot of malicious apps will try and get your browser to automatically open up their website(s) when you start up Chrome. They will also try and take advantage of another setting under System that allows apps to be run even without Chrome being open (more on this one later in this article).
If Open a specific page or set of pages is selected, review the pages listed. If there are any page(s) you didn't add yourself, click on the three horizontal dots that appear on each page's right-hand side and select Remove. You can also add any page you would like to open when you start up Chrome here too automatically.
When you click on Advanced, there is a list of categories that, in my opinion, are just personal preferences. Categories like Languages, Downloads, Printing, and Accessibility are for customizing how Chrome works. Now when it comes to downloads, I prefer having Chrome ask where I want each file to go before downloading them. Again, personal preference.
Second to the last section under Advanced is System. Remember how I told you Chrome could be run without it having to be started? This is where you'll find the setting to disable this feature. If you are using any Google apps that require Chrome, like Google Docs Offline, you will need to leave the Continue running background apps when Google Chrome is closed selected.
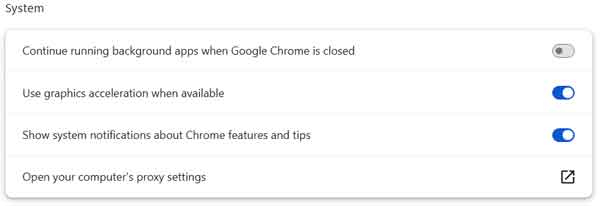
If not, I recommend that you turn this feature off. I've seen adware/malware use this setting to start Chrome when the computer starts up and then controls it remotely. If in doubt, disable it until you are prompted by a Google app to enable it.
The last section under Advanced is Reset and clean up. The link labeled Restore settings to their original defaults will do just that, reset Chrome back to its default, 'out-of-the-box' setup. I'll be just like when you first installed it. The Clean up computer link will scan your computer for unwanted ads, pop-ups, and malware that directly affects Chrome.
The second to the last section is Extensions. This where you will find all of the installed apps that run inside of Chrome. These extend the functionality and usefulness of Chrome. You'll typically find malicious apps that have installed themselves without your knowledge (usually in kiosk mode). It's here that you can either enable, disable, or remove them from Chrome. If you're not sure about an extension, you can always disable it to find out what it did or didn't do inside Chrome. And when you're sure you don't need it or don't remember installing it, just click on the Remove button. If you accidentally remove an extension and want it back, you will have to go through the process of reinstalling it, so be careful.
When you click the Details button for an extension, you will get an option screen. One of the extension options is Allow in incognito for private browsing. Chrome can run in what is called Incognito mode, where it does not save any record of where you have been or what you may have downloaded. If an extension has the option to select Allow in incognito mode, it can be enabled for it. If you use incognito mode, I would defiantly recommend enabling any type of anti-virus, anti-adware, or anti-malware application extension.
The last option to get Chrome back to default and work correctly is to uninstall and reinstall it. I only use this option when all else fails to get it back to full functionality. It can take a little time to do, but if you need to get Chrome fully reset, this may be the only option. There are two (2) ways to uninstall programs in Windows 10; the Settings app or the Control Panel.
Uninstall a program using the Settings app
- Click on the Start
 menu, then Settings (the gear icon), then Apps, then Apps & Features.
menu, then Settings (the gear icon), then Apps, then Apps & Features.
- Scroll down the list of apps in the right-hand column until you find Google Chrome.
- Highlight Google Chrome and click on the Uninstall button.
Uninstall a program using the Control Panel
- In the search box next to the Start
 button, type Control Panel, and click on it from the results.
button, type Control Panel, and click on it from the results.
- Select Uninstall a program (if viewing by category) or Programs and Features (if viewing by icons).
- Highlight Google Chrome and click on the Uninstall button.
Once Google Chrome is uninstalled, restart your computer. When your computer has rebooted and you are logged back in, you will need to remove any traces of Google Chrome before reinstalling it. There are two (2) places where you will need to look for any leftover files; inside your user profile and inside the program files directory. The files inside your user profile are hidden by default, but you can get there quickly by bringing up a Run dialog box (Windows Logo key  + R) and typing or copy / paste the following code:
+ R) and typing or copy / paste the following code:
%userprofile%/AppData/Local/Google
This will open the File Explorer to the location of your Google user settings. If there is a folder named Chrome, go ahead and delete it. Next, you will have to navigate to the location of the Program Files directory and check under the folder named Google. Its location is usually C:\Program Files (x86)\Google, but it may be different if you installed Google Chrome on a different drive. Once you get there, if you find a folder named Chrome, go ahead and delete it. Now you can download and reinstall Google Chrome.