There may come a time when your Windows-based computer starts to run improperly. Installing and uninstalling software, viruses, and malware are just a few things that can corrupt the integrity of system files. When it comes to computer repair on a system running Windows, I always like to check for corrupt system files. You can too with Windows built-in System File Checker (SFC).
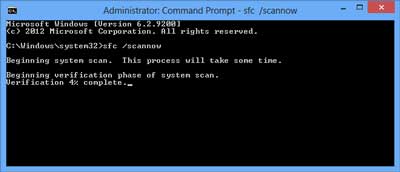
System File Checker running in Command Prompt inside of Windows 8
SFC scans the integrity of all protected system files and replaces incorrect versions with correct Microsoft versions. Everything SFC does is documented in the CBS.log file. If SFC finds any files that it cannot repair, check the CBS.log for more information. See the bottom of command-line syntax(s) and parameter(s) for details on how to view the CBS.log.
Running SFC in Windows Vista, Windows 7, and Windows 8
To ensure that SFC runs with administrator privileges on Windows Vista, Windows 7, and Windows 8, you will need to run it at an administrative Command Prompt.
- Open a Command Prompt with Administrative privileges
How to open a Command Prompt with Administrator privileges in Windows Vista and Windows 7
How to open a Command Prompt with Administrator privileges in Windows 8
- Use the following command line syntax(s) and parameter(s) to run SFC:
sfc [/scannow] [/verifyonly] [/scanfile=<file>] [/verifyfile=<file>] [/offwinddir=<offline windows directory>/offbootdir=<offline boot directory>]
| /scannow |
Scans integrity of all protected system files and repairs files with problems when possible. |
| /verifyonly |
Scans integrity of all protected system files. No repair operation is performed. |
| /scanfile |
Scans integrity of the referenced file, repairs file if problems are identified. Specify full path <file>. |
| /verifyfile |
Verifies the integrity of the file with full path <file>. No repair operation is performed. |
| /offbootdir |
For offline repair specify the location of the offline boot directory. |
| /offwinddir |
For offline repair specify the location of the offline windows directory. |
| /? |
Displays help at the command prompt. |
You can view the CBS.log file in Notepad using the following code at the same administrative Command Prompt used to start SFC.
notepad %systemroot%\Logs\CBS\CBS.log
Running SFC in Windows XP
To use SFC, you will need to open a Command Prompt.
- Click the Start button, then Programs, Accessories, and click on Command Prompt
or
Press  + R. This will bring up the Run dialog box. Type CMD and click OK
+ R. This will bring up the Run dialog box. Type CMD and click OK
- Use the following command line syntax(s) and parameter(s) to run SFC:
sfc [/scannow] [/scanonce] [/scanboot] [/revert] [/purgecache] [/cachesize=<x>]
| /scannow |
Scans all protected system files once. |
| /scanonce |
Scans all protected system files once. |
| /scanboot |
Scans all protected system files every time the computer is restarted. |
| /revert |
Returns the scan to its default operation. |
| /purgecache |
Purges the Windows File Protection file cache and scans all protected system files immediately. |
| /cachesize=<x> |
Sets the size, in MB, of the Windows File Protection file cache. |
| /? |
Displays help at the command prompt. |
When SFC is done, you can view the log file in Notepad using the following code at the same Command Prompt used to start SFC.
notepad %systemroot%\Logs\CBS\CBS.log
f9dfbd1d-ab56-4881-9cd0-32a48c6d6ba1|0|.0|96d5b379-7e1d-4dac-a6ba-1e50db561b04
Did you know that you can use your voice to control your Windows 8 computer? With Speech Recognition inside Windows 8, you can start programs, open menus, click buttons and other objects on the screen, dictate text into documents, and write and send e-mails. Just about everything you can do with your keyboard and mouse can be done with only your voice. All you need is a microphone.
Speech Recognition interface inside of Windows 8
Starting Speech Recognition in Windows 8
- Swipe in from the right side of the screen or press the Windows logo key
 + C to bring up the Charm bar.
+ C to bring up the Charm bar.
- Left-click on Search button in Charm Bar.
- Left-click on Apps in Search.
- Type Speech Recognition in the Search field on the Search pane.
- In the results on the left-hand side, left-click on Windows Speech Recognition.
or
- Go to the Start menu.
- Right-click the Start menu background to bring up the app commands.
- Left-click on All apps.
- Scroll to the Windows Speech Recognition tile and left-click on it.
The first time you run Speech Recognition, you will get the setup wizard. After completing the setup wizard, It is recommended that you go through the Speech Recognition Voice Training.
Using Speech Recognition to control your Windows 8 computer
You can use simple, short commands to control your computer. The following table shows some of the most commonly used Speech Recognition commands. Words that look like this (italic) indicate that you can replace the example word or phrase with similar words and get useful results.
Note: Any time you need to find out what commands to use, say "what can I say?"
| To do this |
Say this |
| Select any item by its name |
Click File; Start; View |
| Select any item or icon |
Click Recycle Bin; Click Computer; Click file name |
| Double tap or double-click any item |
Double-click Recycle Bin; Double-click Computer; Double-click file name |
| Switch to an open app |
Switch to Paint; Switch to WordPad; Switch to program name; Switch application |
| Scroll in one direction |
Scroll up; Scroll down; Scroll left; Scroll right |
| Insert a new paragraph or new line in a document |
New paragraph; New line |
| Select a word in a document |
Select word |
| Select a word and start to correct it |
Correct word |
| Select and delete specific words |
Delete word |
| Show a list of applicable commands |
What can I say? |
| Update the list of speech commands that are currently available |
Refresh speech commands |
| Turn on listening mode |
Start listening |
| Turn off listening mode |
Stop listening |
| Move the Speech Recognition microphone bar |
Move speech recognition |
| Minimize the microphone bar |
Minimize speech recognition |
| View Windows Help and Support content about specific tasks |
How do I do something? For example, say “How do I install a printer?” and a list of Help topics is returned. Note that this command is available only if you're using the U.S. English Speech Recognizer. |
| Insert a new line in the document |
New line |
| Insert a new paragraph in the document |
New paragraph |
| Insert a tab |
Tab |
| Insert the literal word for the next command (for example, you can insert the word "comma" instead of the punctuation mark) |
Literal word |
| Insert the numeral form of a number |
Numeral number |
| Put the cursor before a specific word |
Go to word |
| Put the cursor after a specific word |
Go after word |
| Don't insert a space before the next word |
No space |
| Go to the start of the sentence that the cursor is in |
Go to start of sentence |
| Go to the start of the paragraph that the cursor is in |
Go to start of paragraph |
| Go to the start of the document |
Go to start of document |
| Go to the end of the sentence that the cursor is in |
Go to end of sentence |
| Go to the end of the paragraph that the cursor is in |
Go to end of paragraph |
| Go to the end of the current document |
Go to end of document |
| Select the word in the current document |
Select word |
| Select the word range in the current document |
Select word range; Select word through word |
| Select all text in the current document |
Select all |
| Select a number of words before the location of the cursor |
Select previous 20 words; Select previous 10 words |
| Select a number of words after the location of the cursor |
Select next 20 words; Select next 10 words |
| Select the last text you dictated |
Select that |
| Clear the selection on the screen |
Clear selection |
| Capitalize the first letter of the word |
Caps word |
| Capitalize all the letters of the word |
All caps word |
| Make all the letters in the word lowercase |
No caps word |
| Change the next number of words to uppercase |
Change next 10 words to uppercase |
| Change the next number of words to lowercase |
Change next 10 words to lowercase |
| Delete the previous sentence |
Delete previous sentence |
| Delete the next sentence |
Delete next sentence |
| Delete the previous paragraph |
Delete previous paragraph |
| Delete the next paragraph |
Delete next paragraph |
| Delete the selected or last dictated text |
Delete that |
For more information on Speech Recognition and a complete list of commands, just right-click the Speech Recognition icon on the Desktop Taskbar and select Open Speech Recognition Reference Card.
ceeec54d-e29d-49e1-991d-a4d9b76a15d2|0|.0|96d5b379-7e1d-4dac-a6ba-1e50db561b04
The Task Scheduler inside of Windows 8 automates scheduling system tasks, which perform actions at a specific time or when a particular event occurs, such as checking for updates or running scripts. Task Scheduler provides an organized view of scheduled tasks and a convenient point of access for managing them.
The main screen for Task Scheduler inside of Windows 8
If you use a specific program regularly, you can use the Create Basic Task Wizard to create a task that opens the program for you automatically according to the schedule you choose. For example, if you use a financial program on a specific day each month, you can schedule a task that opens the program automatically, so you don't risk forgetting to open it yourself.
Running Task Scheduler in Windows 8
- On the Start menu, swipe in from the right side of the screen or press the Windows logo key
 + C to bring up the Charm bar.
+ C to bring up the Charm bar.
- Left-click on the Settings button in Charm Bar.
- Left-click on Tiles in Settings.
- Drag the Show/hide administrative tools slider to the Yes position.
- Left-click on the background of the Start menu, making the Charm bar disappear.
- Once the administrative tools appear, left-click on Task Scheduler.
or
- Swipe in from the right side of the screen or press the Windows logo key
 + C to bring up the Charm bar
+ C to bring up the Charm bar
- Left-click on Search button in Charm Bar.
- Left-click on Apps in Search.
- Type Task Scheduler in the Search field on the Search pane
- In the results on the left-hand side, left-click on Task Scheduler.
If you are prompted for an administrator password or confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
Click the Action menu, and then click Create Basic Task.
- Type a name for the task and an optional description, and then click Next.
Select one of the following:
- To select a schedule based on the calendar, click Daily, Weekly, Monthly, or One time, click Next, specify the schedule you want to use, and then click Next.
- To select a schedule based on common recurring events, click When the computer starts or When I log on and then click Next.
- To select a schedule based on specific events, click When a specific event is logged, click Next, specify the event log and other information using the drop-down lists, and then click Next.
- To schedule a program to start automatically, click Start a program, and then click Next. Click Browse to find the program you want to start, and then click Next.
Click Finish.
Triggers and Actions
The two key concepts involved in scheduling a task are triggers and actions. A trigger causes a task to run, and an action is the work that is performed when the task is run. The actions a task can perform include running a program, sending an e-mail message, and showing a message box. For example, you can send an e-mail when a certain event entry is logged in the event log or run a maintenance script when a user logs on to a computer. Occurrences that can trigger a task to run include: a computer starting up, a computer entering an idle state, or a user unlocking a workstation. In addition, you can schedule a task to run at a specified time.
20fd8385-613c-4ad8-8327-5f3c631182b5|0|.0|96d5b379-7e1d-4dac-a6ba-1e50db561b04
During your computer's everyday use, you will accumulate some unnecessary files (temporary setup/internet files, recycle bin, etc.). You can remove these files with the built-in Disk Cleanup (cleanmgr.exe) utility inside of Windows 8. When it comes to computer repair, I use it all the time on my client's systems. And it can be run a couple of different ways and with different options.
Running Disk Cleanup on demand
There are a couple of different ways to run Disk Cleanup on demand. The following procedure cleans up files associated with your user account. You can also use Disk Cleanup to clean up all the files on your computer.
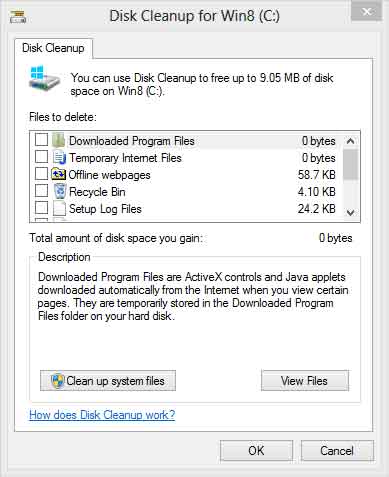
Windows 8 Disk Cleanup dialog box with standard options
- On the Start menu, swipe in from the right side of the screen or press the Windows logo key
 + C to bring up the Charm bar.
+ C to bring up the Charm bar.
- Left-click on the Settings button in Charm Bar.
- Left-click on Tiles in Settings.
- Drag the Show/hide administrative tools slider to the Yes position.
- Left-click on the background of the Start menu, making the Charm bar disappear.
- Once the administrative tools appear, left-click on Disk Cleanup.
or
- Swipe in from the right side of the screen or press the Windows logo key
 + C to bring up the Charm bar.
+ C to bring up the Charm bar.
- Left-click on Search button in Charm Bar.
- Left-click on Apps in Search.
- Type Disk Cleanup in the Search field on the Search pane.
- In the results on the left-hand side, left-click on Disk Cleanup.
After selecting the drive you want to clean, Disk Cleanup scans it for possible files to delete. It then allows you to choose which files to delete. When you click the Clean up system files button, it restarts with a More Options tab. This tab includes two additional ways to free even more disk space:
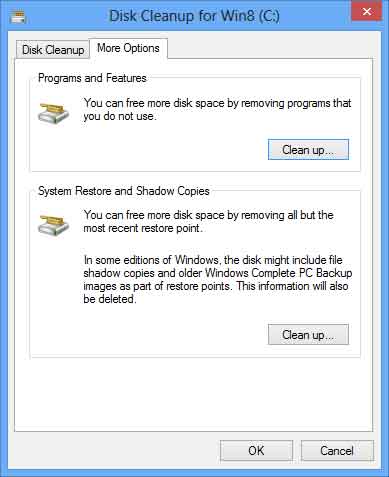
Windows 8 Disk Cleanup dialog box with more options
- Programs and Features. This option opens Programs and Features in Control Panel, where you can uninstall programs that you no longer use. The Size column in Programs and Features shows how much disk space each program uses.
- System Restore and Shadow Copies. With this option, you can delete all but the most recent restore point on the disk.
System Restore uses restore points to return your system files to an earlier point in time. If your computer is running normally, you can save disk space by deleting the earlier restore points.
In some editions of Windows 8, restore points can include previous versions of files, known as shadow copies, and backup images created with Windows Complete PC Backup. These files and images will also be deleted.
Running Disk Cleanup with predefined options
You can also run Disk Cleanup from a command prompt. This gives you the option of predefined settings for running Disk Cleanup as a scheduled task in Task Scheduler or a shortcut on your Desktop or Start menu. Click here for more information on how to open a Command Prompt with Administrator privileges in Windows 8.
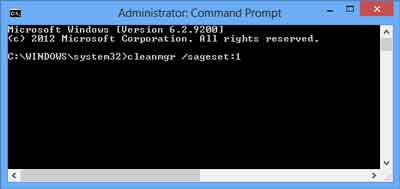
Windows 8 Disk Cleanup run at a Command Prompt with sageset option
You can start the Disk Cleanup tool by running cleanmgr.exe. Disk Cleanup supports the following command-line switches:
- cleanmgr /d driveletter: - This switch selects the drive that you want Disk Cleanup to clean. Note that the /d switch is not used with /sagerun:n.
- cleanmgr /sageset:n - This switch displays the Disk Cleanup Settings dialog box and creates a registry key to store the settings you select. The n value is stored in the registry and allows you to specify different Disk Cleanup tasks to run. The n value can be any integer value from 0 to 65535. To get all the available options when you are using the /sageset switch, you may need to specify the drive letter that contains the Windows installation.
- cleanmgr /sagerun:n - This switch runs the specified tasks that are assigned to the n value by using the /sageset switch. All drives in the computer will be enumerated, and the selected profile will be run against each drive.
To run Disk Cleanup with the /sagerun:n switch in Task Scheduler or in a Desktop or Start menu shortcut, you would use something similar to the following:
C:\Windows\System32\cleanmgr.exe /sagerun:n
3f7e9026-3acc-461e-a77a-0ffdd9779ccb|0|.0|96d5b379-7e1d-4dac-a6ba-1e50db561b04
Desktop and Start menu shortcuts are links to different items. It can be to a program, file, folder, another computer, etc. Here is a quick way to create a Desktop and Start menu shortcut in Windows 8.
- On the Start menu, left-click on the Desktop tile.
- Right-click on any empty area of the Desktop and select New > Folder or Shortcut.
- Right-click on the folder or shortcut you just created and left click Pin to Start.
d58780a6-54b7-44b2-80ab-33568420f9c6|0|.0|96d5b379-7e1d-4dac-a6ba-1e50db561b04