Updated October 15, 2020
Your computer has two types of memory, Random Access Memory (RAM) and Virtual Memory. All programs use RAM, but when there isn't enough RAM for the program you're trying to run, Windows temporarily moves information that would usually be stored in RAM to a file on your hard disk called a Paging File. The amount of data temporarily stored in a paging file is also referred to as virtual memory. Using virtual memory, in other words, moving information to and from the paging file, frees up enough RAM for programs to run correctly.
The more RAM your computer has, the faster your programs will generally run. If a lack of RAM is slowing your computer, you might be tempted to increase virtual memory to compensate. However, your computer can read data from RAM much more quickly than from a hard disk, so adding RAM is a better solution.
If you receive error messages that warn of low virtual memory, you need to either add more RAM or increase your paging file size so that you can run the programs on your computer. Windows usually manages this automatically, but you can manually change the virtual memory size if the default size isn't large enough for your needs.
Change the size of virtual memory
If you receive warnings that your virtual memory is low, you'll need to increase your paging file's minimum size. By default, Windows creates a paging file that can be smaller than the amount of random access memory (RAM) installed on your computer. The recommended minimum page file size should be 1.5X the current amount of RAM, and the maximum size should be 3X the minimum (see custom size below). If you see warnings at these recommended levels, then increase the minimum and maximum sizes.
To open the System Properties, press  + Pause
+ Pause

In the left pane, click Advanced system settings. If you're prompted for an administrator password or confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
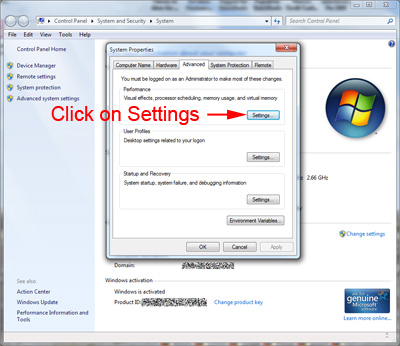
On the Advanced tab, under Performance, click Settings.
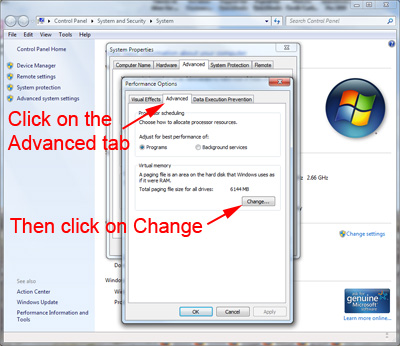
Click the Advanced tab, and then, under Virtual memory, click Change.
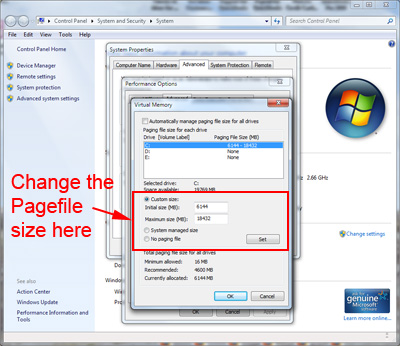
Clear the Automatically manage paging file size for all drives check box.
Under Drive [Volume Label], click the drive that contains the paging file you want to change.
Click Custom size, type a new size in megabytes in the Initial size (MB) or Maximum size (MB) box, click Set, and then click OK. There is a formula for calculating the correct pagefile size. Minimum pagefile size is one and a half (1.5) x amount of memory. Maximum pagefile size is three (3) x minimum pagefile size. Say you have 4 Gb (4,096 Mb) of memory. 1.5 x 4,096 = 6,144 Mb would be the min. pagefile size and 3 x 6,144 = 18,432 Mb would be the max. pagefile size.
Note:
Size increases usually don't require a restart for the changes to take effect, but you'll need to restart your computer if you decrease the size. It is recommended that you don't disable or delete the paging file.
032d137c-0b6d-4f19-99ed-7bb08799ac6e|2|4.5|96d5b379-7e1d-4dac-a6ba-1e50db561b04