One of the most frequent issues I get doing computer repair is the loss of internet connectivity. Yes, a good portion can be attributed to viruses/malware. But there are times when something, plain and simple, goes wrong. A couple of bad settings or corrupt software, and you're not getting on the internet any time soon. Here are three things you can do to restore network connectivity.
Reset the TCP/IP stack and Winsock
If you recently installed or uninstalled software before losing your network connection, it could be some of your TCP/IP settings had been changed. TCP/IP is the internet protocol suite used for the internet and other networks. Resetting them back to default is easy; it requires an administrator command prompt to do it.
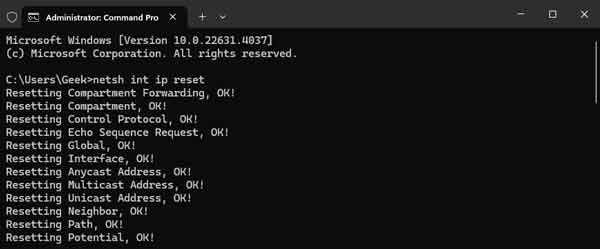
Reset the TCP/IP stack and Winsock interface using an administrator command prompt
The command syntax and accessing an administrator command prompt is different for each version of Windows, so just click on the link below for your version of Windows. And make sure you reset Winsock, too, while you're at it. Winsock defines the interface between applications and the TCP/IP stack. Remember to restart Windows after you reset the TCP/IP stack and Winsock.
Resetting your network adapter in Windows XP
Resetting your network adapter in Windows Vista
Resetting your network adapter in Windows 7
Resetting your network adapter in Windows 8
Resetting your network adapter in Windows 10
Resetting your network adapter in Windows 11
Check security software
Quite often, the problem can be caused by security software that has become corrupt. Most of them have some type of network monitoring, and if it stops working correctly, it could block network access. To check if the problem is with your security software, just open it up, disable it, and try your network connection. If you now have network connectivity, you know that there is something wrong with the software. Try resetting it back to default settings and then enable it. If you still cannot get network access after you reset it, then reinstalling it may be the way to go.
If you open your security software and all you get is a blank white box, it has become corrupt. The same is true if it doesn't open up at all. At this point, uninstalling and reinstalling is the best thing to do. And if you find that it will not uninstall, most anti-virus software vendors have removal tools for their products. Using another computer and a flash drive, search the 'name of the product' + 'removal tool' (example: bogus security removal tool) and download it to the flash drive. Remember to restart your computer after you have run the removal tool.
Reinstall the network adapter(s)
Sometimes, the network adapter settings, wired or wireless, may get corrupted and cause a loss of network connectivity. Uninstalling and then reinstalling the driver(s) will reset it back to manufacturer defaults. Just go into Device Manager and expand the network adapters section. From there, right-click on the adapter you want to reinstall and select Uninstall.
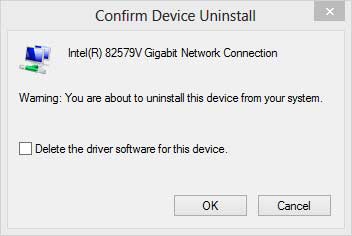
Do not delete the driver when reinstalling the network adapter
When the Confirm Device Uninstall prompt comes up, make sure the 'Delete the driver software for this device' box is unchecked, as you want to keep the driver. Exit Device Manager and restart Windows. When Windows restarts, it will discover the network adapter and automatically install the driver(s) for it.
dc0ba5c3-bb5a-4078-9e3e-d1b7f2024848|1|5.0|96d5b379-7e1d-4dac-a6ba-1e50db561b04