Updated October 2, 2022
Remember the old saying, "A place for everything and everything in its place"? The same holds for your files inside of Windows 10 and Windows 11. And managing your data in Windows 10 and Windows 11 can be a breeze when you use Libraries.
One of my favorite Windows file/folder organization features has to be Libraries. Libraries are nothing more than a collection of shortcuts to the original file/folder locations. But the places can be on your local computer or a network drive. Once you add a location to a library, it's just one click away inside of File Explorer.
Now let's not confuse user file folders with Libraries. User file folders are actual folders; Libraries are collections of shortcuts to user file folders. Your user files are already included in the Libraries by default. User file folders must be located on your computer, but Libraries can be shortcuts to both local and network file folders.
It's somewhat ironic that one of the coolest features that I can think of inside of Windows 10 and Windows 11 is hidden by default. But you can un-hide Libraries in just seconds. Here's how:
How to enable the Library view in Windows 10
- Open File Explorer by either
- Left-clicking on the File Explorer icon (manilla folder) on the Taskbar.
- Left-clicking the Start button, scrolling down and expanding the Windows System folder and left-clicking on File Explorer.
- Right-click on the Start button and left-click on File Explorer from the Power User menu.
- Press the Windows logo key
 + E.
+ E.
- Left-click on the View tab on the top of the Ribbon.
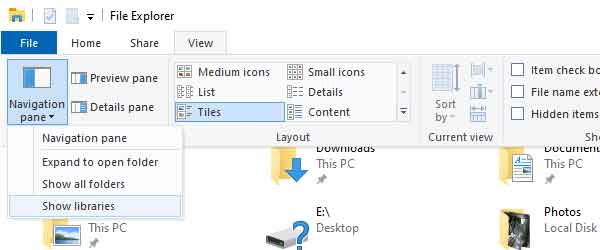
- Left-click on the Navigation pane button and left-click on Show libraries.
How to enable the Library view in Windows 11
- Open File Explorer by either
- Left-clicking on the File Explorer icon (manilla folder) on the Taskbar.
- Left-clicking the Start button, left-clicking on All apps, scrolling down and left-clicking on File Explorer.
- Right-click on the Start button and left-click on File Explorer from the Power User menu.
- Press the Windows logo key
 + E.
+ E.
- Left-click on the See more three horizontal dots (...) in the upper right-hand corner
- In the context menu that appears, left-click on Options.
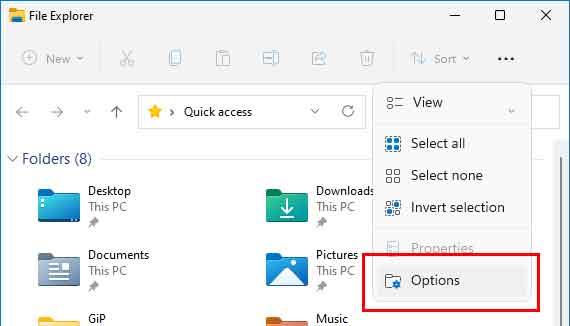
The Folder Options dialog box will appear.
- On the Folder Options dialog box, left-click on the View tab.
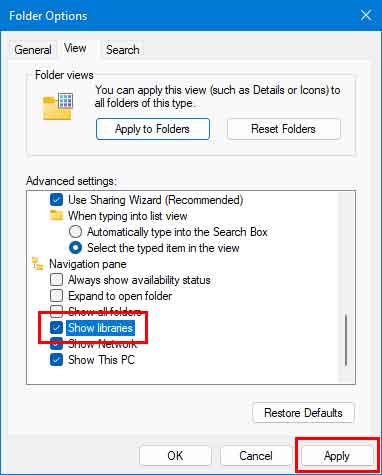
Scroll to the bottom of the Advanced settings, select Show libraries, and then left-click the Apply button.
How to modify Library properties in Windows 10 and Windows 11
We are all familiar with files and folders, but when Windows 7 came out, we got another way to manage them, Libraries. Libraries are where you go to manage your documents, music, pictures, and other files. You can browse your data the same way you would in a folder, or view your files arranged by properties like date, type, and author.
In some ways, a Library is similar to a folder. For example, when you open a Library, you'll see one or more files. However, unlike a folder, a Library gathers data stored in several locations. This is a subtle but significant difference. Libraries don't hold your files, just shortcuts to them. Libraries monitor folders containing your data and let you access and arrange the files differently. For instance, if you have music files in folders on your hard disk and an external drive, you can access all of your music files at once using the Music Library.
Windows 10 and Windows 11 have four (4) default libraries (Documents, Music, Pictures, and Videos) and include links to your user files by default. Remember that you can add up to fifty (50) folders to a Library. And if you like, you can also create your own Libraries. Here are some other ways you can modify an existing Library.
- Include or remove a folder. Libraries gather content from included folders or Library locations.
- Change the default save location. The default save location determines where an item is stored when it's copied, moved, or saved to the Library.
- Change the type of file a library is optimized for. Each Library can be optimized for a specific file type (such as music or pictures). Optimizing a Library for a particular file type changes the available options for arranging your files.
How to add a folder to a Library in Windows 10 and Windows 11
- Open File Explorer (see enabling Library view).
- Right-click on the Library you'd like to change and select Show more options (Windows 11), Properties.
- Below the Library Locations box, click on Add, navigate to and highlight the folder you want to add to the Library, and left-click on Include folder.
- Left-click OK.
How to change a Library's default save location in Windows 10 and Windows 11
A Library's default save location determines where an item will be stored when it's copied, moved, or saved to the Library. You will need two or more folders in a Library to change the default save location.
- Open File Explorer (see enabling Library view).
- Right-click on the Library you'd like to change and select Show more options (Windows 11), Properties.
- Select the Library location you want as default, left-click on Set save location, and then left-click Apply.
- Left-click OK.
How to change the type of files a Library is optimized for in Windows 10 and Windows 11
Each Library can be optimized for a specific file type (such as music or pictures). Optimizing a Library for a particular kind of file changes the available options for arranging the data in that Library.
- Open File Explorer (see enabling Library view).
- Right-click on the Library you'd like to change and select Show more options (Windows 11), Properties.
- In the Optimize this library for list, select a file type and then left-click Apply.
- Left-click OK.
How to create a new Library in Windows 10 and Windows 11
- Open File Explorer (see enabling Library view).
- Right-click on Libraries and select Show more options (Windows 11), then New, then Library.
- Enter a name for the new Library, and then press Enter.
How to remove a folder from a Library in Windows 10 and Windows 11
If you don’t need a folder in a Library anymore, you can remove it. When you remove a folder from a Library location (shortcut), the folder and everything in it is still kept in its original location. Remember that when you delete a folder from a Library (folder), the folder and everything in it is deleted in its original location.
- Open File Explorer (see enabling Library view).
- Right-click on the Library you'd like to change and select Show more options (Windows 11), Properties.
- In the Library Locations dialog box, left-click on the folder you want to remove, left-click Remove, and then left-click OK.
How to add a network folder that is not indexed to a Library in Windows 10 and Windows 11
There will be times when you cannot get a shared network folder added to a Library due to indexing issues, and I found a way to get around this problem by creating a symbolic link.
- Open File Explorer (see enabling Library view).
- Left-click on This PC and create a folder on your drive for your network folders, for example, c:\share.
- Create another folder within that folder, for example, c:\share\music.
- Right-click the subfolder you just created and select Show more options (Windows 11), Include in library, and then select the library to which you want to add the folder or create a new Library.
- Delete the folder.
- Open a Command Prompt with Administrator privileges
- Enter mklink /d, and then enter the path of the folder you just deleted and the path of the network folder. For example, mklink /d c:\share\music \\server\music. If either of the folder names has spaces, encase the path(s) inside of quotes. For example, mklink /d "c:\shared files\music" "\\server\shared music". This creates what is called a symbolic link.
Here's how to create a symbolic link in Windows 8. It's the same procedure for Windows 10 and Windows 11.
4ede9479-bfb2-4661-9fce-12097089a4e5|2|3.0|96d5b379-7e1d-4dac-a6ba-1e50db561b04