Updated January 31, 2021. Microsoft's Enhanced Mitigation Experience Toolkit reached the end of its life on July 31, 2018, and is no longer available for download.
Let's face it, some of the software we use on a daily basis has become subject to security vulnerabilities and exploits. Software manufacturers do their best to develop and test fixes / patches as fast as possible, but this can take time. A lot of users just cannot keep up with all of the updates and hotfixes. A few years ago Microsoft released the Enhanced Mitigation Experience Toolkit (EMET) to deal with just this issue.
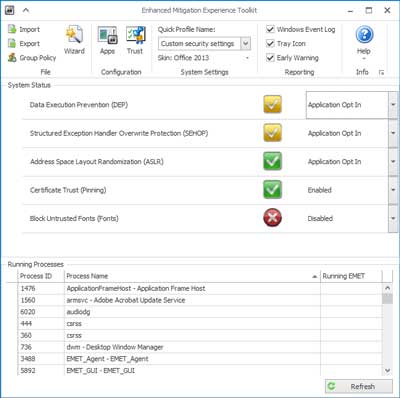
View of the main screen inside EMET 5.5
So what is EMET? EMET monitors selected programs (Internet Explorer, Microsoft Office, etc.) for known attack actions and techniques. When one of the several pseudo mitigation technologies is triggered, EMET will either block the programs' access to the resource it is trying to reach or just terminate it. EMET expands on the technologies that Microsoft implemented with Data Execution Prevention (DEP), which has been included in the Windows operating system since Windows XP SP2. It will also validate digitally signed SSL certificates inside of Internet Explorer.
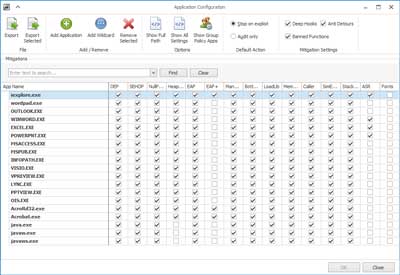
View of the application configuration screen inside EMET 5.5
So how does EMET work? EMET acts as a shim between the program being monitored and the operating system. The monitored program thinks it's talking directly to the operating system, but it's actually talking to it through EMET. EMET comes with predefined profiles for some of the more common programs like Microsoft Office, Internet Explorer, Adobe Acrobat and Java. You can also add to the predefined profiles or create your own. I recommend that you monitor any program that can open files on or from the Internet.
What security exploits are currently covered
Here's is the current list of mitigations EMET 5.5 currently looks for.
- Attack Surface Reduction (ASR) Mitigation
- Export Address Table Filtering (EAF+) Security Mitigation
- Data Execution Prevention (DEP) Security Mitigation
- Structured Execution Handling Overwrite Protection (SEHOP) Security Mitigation
- NullPage Security Mitigation
- Heapspray Allocation Security Mitigation
- Export Address Table Filtering (EAF) Security Mitigation
- Mandatory Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) Security Mitigation
- Load Library Check - Return Oriented Programming (ROP) Security Mitigation
- Memory Protection Check - Return Oriented Programming (ROP) Security Mitigation
- Caller Checks - Return Oriented Programming (ROP) Security Mitigation
- Simulate Execution Flow - Return Oriented Programming (ROP) Security Mitigation
- Stack Pivot - Return Oriented Programming (ROP) Security Mitigation
- Windows 10 untrusted fonts
What programs should you harden / mitigate
You only want to harden / mitigate certain programs that are targeted on a regular basis. Web browsers like Chrome, Firefox and Internet Explorer, production / office programs like Microsoft Word, Excel and PowerPoint, e-mail clients like Outlook and Windows Live Mail are some of the few. I recommend that you harden any program that can open files on or from the Internet.
What programs should you not harden / mitigate
You should never configure EMET to monitor anti-virus, anti-malware, intrusion prevention / detection software, debuggers, software that handles Digital Rights Management (DRM) technologies or software that uses anti-debugging, obfuscation, or hooking technologies.
Installation notes
New installation: Just download EMET and install
Upgrade install: Since the registry keys for EMET changed with this version, you can either export your existing EMET settings using the method in the 'What's new' section below, download the converter or reconfigure all of the program settings. With the drastic change with the EMET data format inside of the registry, I think that it would be just easier to reconfigure EMET then try the export / import method. Either way, remember to uninstall any older version of EMET and restart your computer before you install this version.
What's new in EMET 5.5?
- Full-featured GPO management, compatible with reporting and compliance requirements
- Command line: new syntax and options
- Implementation of certificate pinning now based on root CA thumbprints. Exceptions logic removed.
- Export and Import now memorize path
- EMET registry has been refactored. To convert settings from previous versions of EMET (including EMET 5.5 Beta), registry values must be saved in a file then imported back with the use of the converter PowerShell script after EMET 5.5 is installed. Here are the steps to follow:
- Export settings. With elevated PowerShell, run the following command:
.\Migrate-EmetSettings.ps1 -RegFile .\NewEmetSettings.reg -MissingCertCsv .\MissingCerts.csv PowerShell script Migrate-EmetSettings.ps1 is provided with EMET 5.5 RTM. It includes documentation about its usage.
- Uninstall former version of EMET.
- Install EMET 5.5 RTM. When asked to choose between Use recommended settings and Configure manually later, chose option Configure manually later.
- Import settings. With elevated PowerShell, run the following command:
reg.exe import .\NewEmetSettings.reg
Supported Operating Systems
Windows 10 , Windows 7, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Vista
- EMET 5.5 requires .NET Framework 4.5.
- For Internet Explorer 10 on Windows 8 you need to install KB2790907 - a mandatory Application Compatibility update that has been released on March 12th, 2013 or any other Application Compatibility updates for Windows 8 after that
fb155e78-21ea-4dd1-8d8f-4bdbd978b7ee|0|.0|96d5b379-7e1d-4dac-a6ba-1e50db561b04