Searching in Windows 7 can be as simple as typing a few letters in the search box, but there are also advanced searching techniques that you can use. You don't have to know these techniques to search for your files, but they can be helpful depending on where your searching and what you're searching for.
Adding search filters
Search filters are a new feature in Windows 7 that makes searching for files by their properties (such as by author or by file size) much more straightforward.
To add a search filter to your search
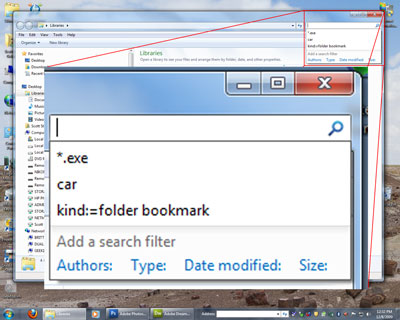
The search box in a folder or library
- Open the folder, library, or drive that you want to search.
- Click in the search box, and then click a search filter (for example, Date taken: in the Pictures library).
- Click one of the available options. (For example, if you clicked Date taken: choose a date or a date range.)
When you add a search filter, you'll notice that unigue keywords are automatically added to the search box. These keywords can help you refine your search by narrowing possibilities.
You can add multiple search filters to a search, or even mix search filters with standard search terms to further refine your search.
You can use two search filters to search for a picture tagged with "family" that was taken a long time ago.
Depending on where you're searching, only certain search filters are available. For example, if you're searching the Documents library, you'll see different search filters than you would in the Pictures library. You can't specify which search filters you'll see, but you can change the type of file a library is optimized for. This will, in turn, change which search filters are available when searching that library.
Using keywords to refine a search
When searching for a specific file, most people type the file's name in the search box. But you can also search for a file based on its contents or properties. Type "summer," for example, and it will find files named "sunset in summer.jpg," files tagged with "summer," and files with the word "summer" in the content. This broad approach to search usually helps you find your file quickly.
You can search by any file property. For example, if you know a file's type, you can enter the file extension ("JPG" for example) in the search box. Or, if you don't know the extension, you can type "document," "picture," or "music" to search for files of a specific kind.
If you want to search more selectively, you can type specific keywords (such as "Name:" or "Tag:") in the search box to specify which file property to search. This typically involves typing a property name followed by a colon and then typing a value. Here are some examples of search terms:
Example search term |
Use this to |
Name:Sunset |
Find only files that have the word sunset in the file name. |
Tag:Sunset |
Find only files that are tagged with the word sunset. |
Modified:05/25/2006 |
Find only files that were modified on that date. You can also type Modified:2006 to find files changed at any time during that year. |
Another way to refine a search is to use Boolean filters to combine search words using simple logic. When you type Boolean filters such as AND or OR, you need to use all capital letters.
| Boolean filter |
Example search term |
Use this to |
AND |
tropical AND island |
Find files that contain both words "tropical" and "island" (even if those words are in different places within the file). |
NOT |
tropical NOT island |
Find files that contain the word "tropical," but not "island." |
OR |
tropical OR island |
Find files that contain either of the words "tropical" or "island." |
Quotes |
"tropical island" |
Find files that contain the exact phrase "tropical island." |
Parentheses |
(tropical island) |
Find files that contain both words "tropical" and "island" in any order. |
> |
date: > 01/05/06 |
Find files with an attribute more than or later than a specific value, such as after 01/05/06. |
< |
size: < 4 MB |
Find files that have an attribute less than or earlier than a specific value, such as fewer than 4 MB. (You can also specify other sizes, such as KB and GB.) |
You can even combine Boolean filters with other search terms. The following table shows how you can get very different results using the same search words but different Boolean filters. (Note how the use of parentheses can change the effect of a search term.)
| Example search term |
Use this to |
author: Charlie AND Herb |
Find files that are authored by Charlie as well as any files that include Herb in the file name or in any file property. |
author: (Charlie AND Herb) |
Find only files that are authored by both names. |
author: "Charlie Herb" |
Finds only files that are authored by someone with exactly this name. |
Using natural language search
You can turn on Natural language search to perform searches in a simpler way, without using colons and without the need to enter AND and OR in capital letters. For example, compare these two searches:
| Without natural language |
With natural language |
kind: music artist: (Beethoven OR Mozart) |
music Beethoven or Mozart |
kind: document author: (Charlie AND Herb) |
documents Charlie and Herb |
To turn on natural language search
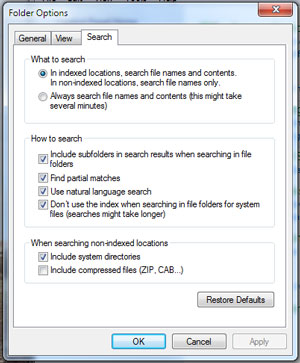
The Search tab under Folder Options
- Click on the Start menu, then Control Panel, then Appearance and Personalization, then Folder Options.
- Click the Search tab.
- Select the Use natural language search checkbox.
Even with natural language search turned on, you can continue to use the search box the same way. If you want to use Boolean filters or search keywords, you can. The difference is that you can also enter searches using a less formal method. Here are some examples:
- e-mail today
- documents 2006
- author Susan
- pictures vacation
Note:
When you turn on natural language search, some searches might give more results than you expect. For example, if you search for "e-mail today", you will see all messages sent today as well as any messages with the word "today" in the contents.
4d640323-c873-4b28-a917-6114b9a4a8d2|0|.0|96d5b379-7e1d-4dac-a6ba-1e50db561b04